INVESTIGATIONAL CDC7 INHIBITOR
monzosertib (AS-0141)
Potential first-in-class CDC7 inhibitor
- TARGET
- CDC7 (cell division cycle 7) kinase
- INDICATION
- Solid Tumors/Hematological Malignancies
- MODALITY
- Small molecule
- DEVELOPMENT STAGE
- Phase 1 in Japan
- CLINICAL TRAIL INFORMATION
- https://jrct.mhlw.go.jp/en-latest-detail/jRCT2031210072
Mechanism of Action
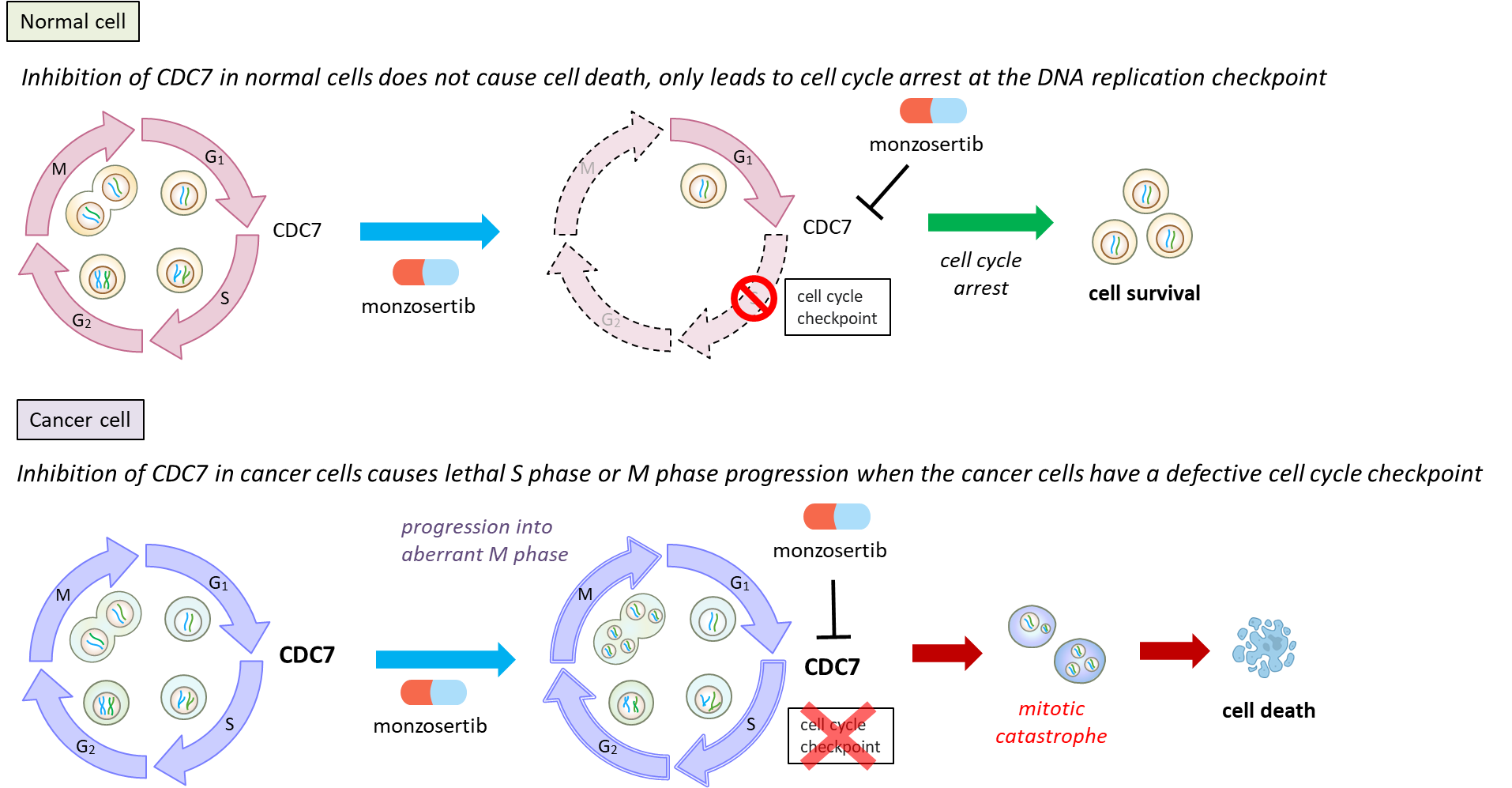
CDC7 is a serine-threonine kinase that plays a critical role in DNA synthesis and is required for the activation of DNA replication origins throughout the S phase of the cell cycle. Inhibition of CDC7 in cancer cells causes lethal S phase or M phase progression, whereas normal cells survive, most likely through induction of cell cycle arrest at the DNA replication checkpoint. It has been reported in the literature that CDC7 is overexpressed in many cancers including colon cancer, kidney cancer, bladder cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer and leukemia.
Preclinical Study
Monzosertib has a unique inhibitory mechanism for CDC7 kinase (time-dependent inhibition). Monzosertib exhibited a potent anti-proliferative activity against various cancer cell lines including solid and blood cancers with minimal effects against normal cells. In several human tumor xenograft models, oral administration of monzosertib demonstrated strong anti-tumor efficacy. Preclinical studies demonstrated that combinations with standard of care treatments exerted strong synergistic effects in hematological malignancies.
Clinical Study
Monzosertib is currently being evaluated in an open-label Phase 1 study in Japan in patients with advanced, metastatic, relapsed or refractory malignancies including solid tumors and blood cancers. This study consists of two parts for each of solid tumors and blood cancers: a dose escalation part aiming to identify the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and/or recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D) of monzosertib and an expansion cohort aiming to ensure the appropriateness of the RP2D and to evaluate the preliminary anti-tumor effect.
Currently, the dose expansion part is underway for solid tumors, while the dose escalation part is in progress for blood cancers.
References
- Triplet combination of monzosertib, a potent CDC7 inhibitor, with DNMT and BCL2 inhibitors is highly active in human AML xenograft mouse models, American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2025
- Synergistic effect of the CDC7 inhibitor, monzosertib (AS-0141) with current therapies in AML models, American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2024
- CDC7 kinase inhibitors: a survey of recent patent literature (2017-2022). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2023 Jul-Dec;33(7-8):493-501.
- Discovery of AS-0141, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of CDC7 Kinase for the Treatment of Solid Cancers. J Med Chem. 2021 Oct 14;64(19):14153-14164.
- Discovery of novel furanone derivatives as potent Cdc7 kinase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Apr 21;130:406-418.
- Drug design with Cdc7 kinase: a potential novel cancer therapy target. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2009 Feb 6;2:255-264.
