- Home
- Cell-Based Assay Services
- NanoBRET™ TE Intracellular Kinase Assay Services
- NanoBRET™ TE Intracellular CDK Panel Service
NanoBRET™ TE Intracellular CDK Panel Service
The cell cycle defines the sequential molecular processes that ensure correct cell division. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) play key roles in these cell cycle events, and in the integration of extracellular and intracellular signals to modulate gene transcription and cell division. CDKs represent attractive drug discovery targets for oncology in particular. However, the evaluation of compound potency against some CDKs in biological assays can be misleading due to their unique dependence on a regulatory subunit - a cyclin, as well as other unknown cellular factors potentially affecting CDK activities.
Carna’s NanoBRET™ TE Intracellular CDK Panel Assay consists of 24 CDK targets. It is an ideal tool to examine the specificity of your CDK inhibitor across an extensive set of CDK family kinases: in the presence of the cyclin subunit; in a cellular environment; and in a unified assay format. The compound’s engagement with each CDK is quantitatively measured inside living HEK293 cells, which provides a snapshot of your compound’s selectivity across all the CDK targets in the panel.
These studies are performed at one concentration point in duplicate or can be customised to meet any particular desired conditions or specific selection of CDK targets.
Carna's Cell-based CDK Panel Assay brings out different selectivity of your compound!
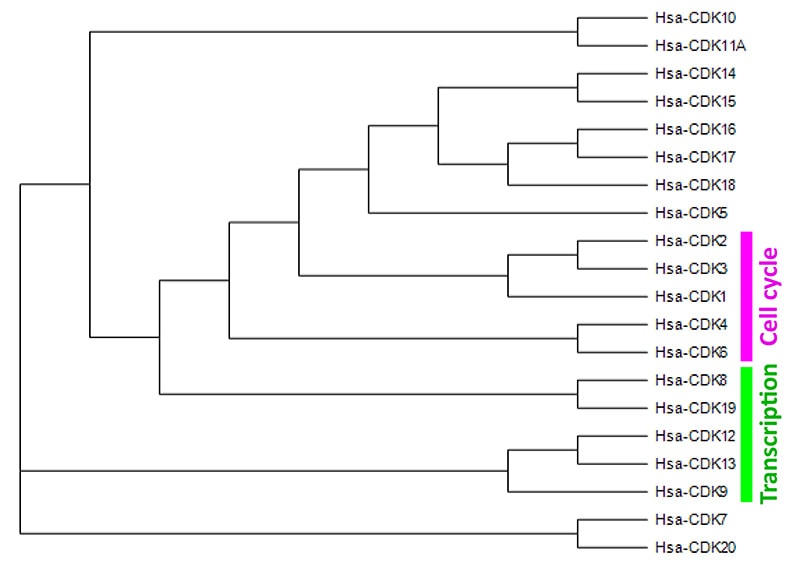
CDK Phylogenic Tree
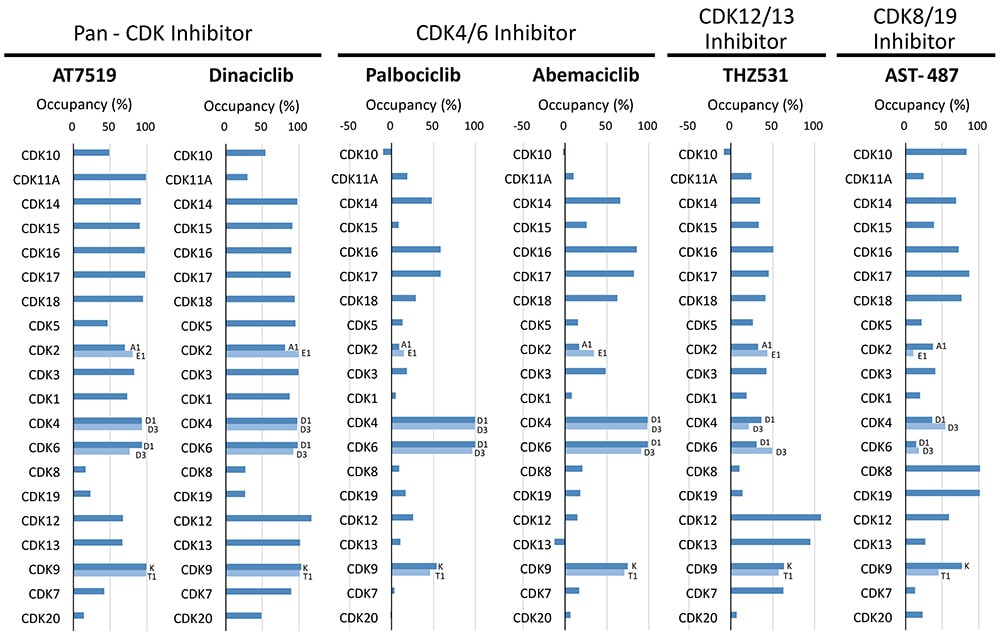
NanoBRET™ TE Intracellular CDK Panel Assay reveals each selectivity at 10 μM conc. of pan-CDK inhibitors (AT7519, dinaciclib), CDK4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, abemaciclib), CDK12/13 inhibitor (THZ531), and CDK8/19 inhibitor (AST-487).
[CDKs - Cyclin-dependent Kinases ]
The progression throughout the cell cycle is regulated by a group of serine/threonine kinases called the CDK family, whose activity is regulated by their association with partner subunits known as cyclins. In addition to those kinases involved in cell cycle regulation (such as CDKs 1, 2, 4 and 6), other CDK members (such as CDKs 7, 8, 9, 12 and 13) play a role in the regulation of transcription through phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II (RNAP II, Pol II). CDK family members also play important roles in DNA damage repair, epigenetic regulation, stem cell self-renewal, neuronal functions, and spermatogenesis, however, the roles of many of the CDK family kinases, including CDKs 5, 10, 11, 14-18 and 20, have yet to be understood fully.
CDK Panel Kinase Targets
Please refer to sample data of each CDK target from here.
- <Guide for Service Customers>
- Service Flow
- Compound Handling and Shipping
- Application Form for NanoBRET™ Cell-based Assay
